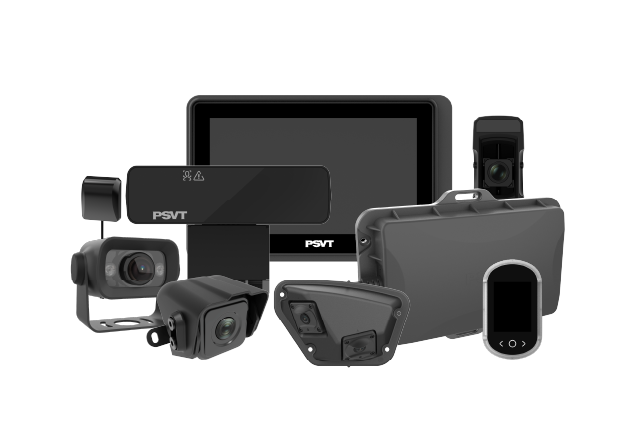
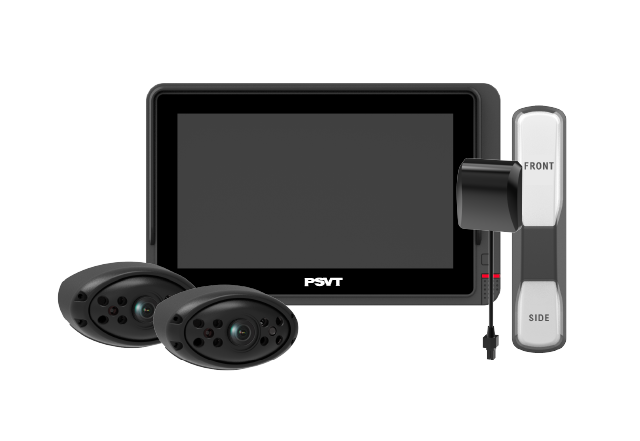
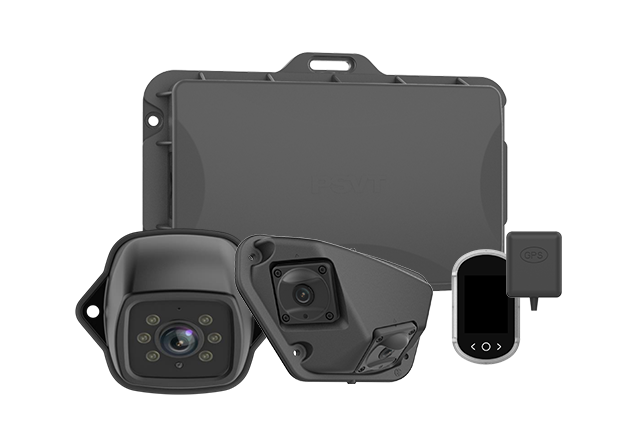
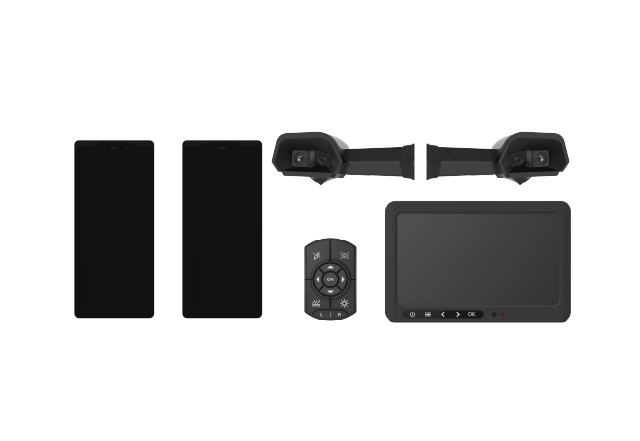
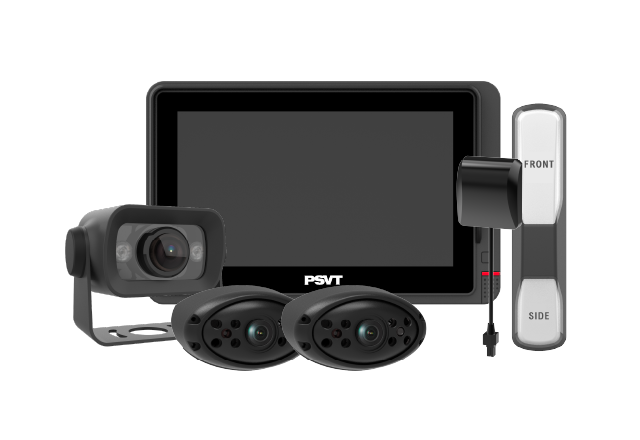
Blind spot detection systems have become a critical feature in modern vehicle safety. These advanced systems use a combination of sensors and cameras to monitor areas around a vehicle that are difficult for the driver to see, providing alerts when another vehicle enters these blind spots. This technology has proven to reduce lane-change accidents and injuries, making roads safer for everyone. Research shows a 14% decrease in lane-changing collisions and a 23% reduction in injury rates related to such crashes.
What is a Blind Spot Detection System?
At its core, a blind spot detection system utilizes radar, ultrasonic sensors, and cameras to monitor the vehicle’s blind spots — areas typically not visible through mirrors or direct sight. The system activates alerts when a vehicle enters these zones, alerting the driver to the potential risk. This technology plays a crucial role in preventing accidents, enhancing driver awareness, and ensuring safer driving.
Why Blind Spot Detection is Crucial for Vehicle Safety
According to the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety (IIHS), blind spot detection systems reduce lane-change accidents by 14% and decrease related injuries by 23%. The technology helps drivers spot fast-approaching vehicles in their blind spots, giving them time to make safer decisions. While the system is highly effective, challenges remain, particularly when it comes to detecting fast-moving vehicles or motorcycles. However, the overall safety benefits far outweigh these limitations, significantly enhancing road safety.
BSD Core Components and Technologies
Radar Sensors
How Does Radar Sensors Work:
Radar sensors are essential in blind spot detection. These sensors emit radio waves that bounce off nearby vehicles and objects. By measuring the time it takes for the waves to return, the system calculates the distance and speed of these objects, identifying potential hazards in the blind spot.
Advantages of Radar Sensors:
Radar sensors excel in various weather conditions, including rain, fog, or snow. They are also highly accurate, providing reliable distance measurements even in low-visibility conditions. Radar sensors are particularly useful for detecting fast-moving vehicles, offering timely alerts to drivers.
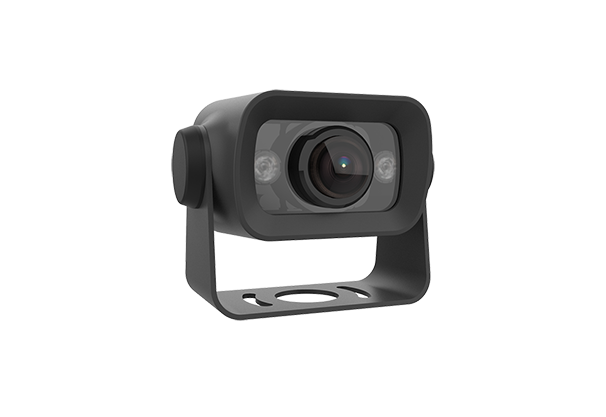
Cameras
Capturing Visual Data:
Cameras capture real-time visual data around the vehicle, which is processed by the system to identify vehicles in the blind spots. Cameras are typically used in conjunction with radar or ultrasonic sensors to provide a more comprehensive monitoring system.
Integration with Other Systems:
Cameras work seamlessly with other vehicle systems, such as lane-keeping assist. This integration improves the accuracy of the system and enhances overall vehicle safety, especially with features like 360-degree camera views.
Ultrasonic Sensors
How They Work:
Ultrasonic sensors use high-frequency sound waves to detect nearby objects. The system calculates the distance based on the time it takes for the sound waves to return after hitting an object.
Use Cases:
Ultrasonic sensors are especially useful in low-speed scenarios like parking. These sensors detect objects that are very close to the vehicle, making them ideal for tight spaces. Many modern vehicles combine radar, ultrasonic sensors, and cameras for optimal blind spot detection performance.
How Blind Spot Detection Systems Work Together
Detection Area
The detection area is the region around the vehicle that the system monitors, typically covering one lane width on each side of the vehicle. These areas are critical to identify potential hazards that are not visible through the driver’s mirrors.
Sensors like radar, cameras, and ultrasonic units work together to monitor these zones, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the blind spots.
Types of Alerts
- Visual Alerts: Visual alerts, often displayed on the side mirrors or dashboard, provide immediate warnings when a vehicle enters the blind spot. These lights or icons activate as a clear signal to the driver.
- Auditory Alerts: Beeps or warning sounds notify the driver when a vehicle is in the blind spot or when the driver attempts to change lanes while a hazard is present.
- Haptic Feedback: Vibrations in the steering wheel or seat serve as tactile alerts, enhancing safety by offering a physical sensation to the driver.
Advanced Features of Blind Spot Detection Systems
Automatic Braking
How It Works:
Automatic braking is an advanced feature that uses sensors to detect imminent collisions and triggers the vehicle’s brakes. This system helps avoid accidents by slowing or stopping the vehicle when a fast-approaching vehicle is detected in the blind spot or when the driver fails to react quickly enough.
Use Cases:
Automatic braking proves particularly useful when a driver attempts a lane change and an approaching vehicle is detected too late. It also activates in heavy traffic to prevent rear-end collisions, reducing accidents by up to 20% in certain scenarios.
Steering Assistance
How It Works:
Steering controls can intervene when the system detects a potential collision. The system can adjust the steering to help keep the vehicle in its lane, preventing accidents due to lane changes or swerving.
Benefits:
Steering assistance works in tandem with other safety features, ensuring that the vehicle remains within its lane and avoids collisions. According to the IIHS, blind spot monitoring kits prevent up to 50,000 crashes and nearly 16,000 injuries annually.
Benefits of Blind Spot Detection Systems
Enhanced Road Safety
By monitoring areas that are difficult for drivers to see, blind spot detection systems significantly reduce the risk of accidents, particularly lane-change collisions. Vehicles equipped with these systems experience fewer accidents and injuries, creating a safer driving environment for everyone.
Increased Driver Awareness
The alerts provided by blind spot detection systems increase driver awareness by constantly monitoring blind spots and providing immediate feedback. Studies have shown that drivers feel more confident and secure with these systems in place, as they help eliminate blind spots and reduce the risk of missing potential hazards.
Public Perception and Adoption
Public surveys reveal that blind spot monitoring is one of the most appreciated car safety technologies. Many drivers value the peace of mind that comes from knowing their vehicle is continuously monitoring for blind spot risks.
Conclusion
Blind spot detection systems are a transformative advancement in vehicle safety technology. By combining radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors, these systems provide a comprehensive view of areas that drivers cannot see. With real-time alerts and advanced features like automatic braking and steering assistance, blind spot detection not only prevents accidents but also makes roads safer for everyone.